2 changed files with 281 additions and 53 deletions
Unified View
Diff Options
-
+241 -0README.2.2.md
-
+40 -53README.md
+ 241
- 0
README.2.2.md
View File
| @@ -0,0 +1,241 @@ | |||||
| # CAP [中文](https://github.com/dotnetcore/CAP/blob/develop/README.zh-cn.md) | |||||
| [](https://travis-ci.org/dotnetcore/CAP) | |||||
| [](https://ci.appveyor.com/project/yuleyule66/cap) | |||||
| [](https://www.nuget.org/packages/DotNetCore.CAP/) | |||||
| [](https://www.nuget.org/packages/DotNetCore.CAP/) | |||||
| [](https://github.com/dotnetcore) | |||||
| [](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dotnetcore/CAP/master/LICENSE.txt) | |||||
| CAP is a library based on .Net standard, which is a solution to deal with distributed transactions, also has the function of EventBus, it is lightweight, easy to use, and efficiently. | |||||
| ## OverView | |||||
| In the process of building an SOA or MicroService system, we usually need to use the event to integrate each services. In the process, the simple use of message queue does not guarantee the reliability. CAP is adopted the local message table program integrated with the current database to solve the exception may occur in the process of the distributed system calling each other. It can ensure that the event messages are not lost in any case. | |||||
| You can also use the CAP as an EventBus. The CAP provides a simpler way to implement event publishing and subscriptions. You do not need to inherit or implement any interface during the process of subscription and sending. | |||||
| This is a diagram of the CAP working in the ASP.NET Core MicroService architecture: | |||||
|  | |||||
| > The solid line in the figure represents the user code, and the dotted line represents the internal implementation of the CAP. | |||||
| ## Getting Started | |||||
| ### NuGet | |||||
| You can run the following command to install the CAP in your project. | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| If you want use Kafka to send integrating event, installing by: | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.Kafka | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| If you want use RabbitMQ to send integrating event, installing by: | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.RabbitMQ | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| CAP supports SqlServer, MySql, PostgreSql as event log storage. | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| // select a database provider you are using, event log table will integrate into. | |||||
| PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.SqlServer | |||||
| PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.MySql | |||||
| PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.PostgreSql | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| ### Configuration | |||||
| First,You need to config CAP in your Startup.cs: | |||||
| ```cs | |||||
| public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) | |||||
| { | |||||
| //...... | |||||
| services.AddDbContext<AppDbContext>(); | |||||
| services.AddCap(x => | |||||
| { | |||||
| // If you are using EF, you need to add the following configuration: | |||||
| // Notice: You don't need to config x.UseSqlServer(""") again! CAP can autodiscovery. | |||||
| x.UseEntityFramework<AppDbContext>(); | |||||
| // If you are using ado.net,you need to add the configuration: | |||||
| x.UseSqlServer("Your ConnectionStrings"); | |||||
| x.UseMySql("Your ConnectionStrings"); | |||||
| x.UsePostgreSql("Your ConnectionStrings"); | |||||
| // If you are using RabbitMQ, you need to add the configuration: | |||||
| x.UseRabbitMQ("localhost"); | |||||
| // If you are using Kafka, you need to add the configuration: | |||||
| x.UseKafka("localhost"); | |||||
| }); | |||||
| } | |||||
| public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app) | |||||
| { | |||||
| //..... | |||||
| app.UseCap(); | |||||
| } | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| ### Publish | |||||
| Inject `ICapPublisher` in your Controller, then use the `ICapPublisher` to send message | |||||
| ```c# | |||||
| public class PublishController : Controller | |||||
| { | |||||
| [Route("~/publishWithTransactionUsingEF")] | |||||
| public async Task<IActionResult> PublishMessageWithTransactionUsingEF([FromServices]AppDbContext dbContext, [FromServices]ICapPublisher publisher) | |||||
| { | |||||
| using (var trans = dbContext.Database.BeginTransaction()) | |||||
| { | |||||
| // your business code | |||||
| //If you are using EF, CAP will automatic discovery current environment transaction, so you do not need to explicit pass parameters. | |||||
| //Achieving atomicity between original database operation and the publish event log thanks to a local transaction. | |||||
| await publisher.PublishAsync("xxx.services.account.check", new Person { Name = "Foo", Age = 11 }); | |||||
| trans.Commit(); | |||||
| } | |||||
| return Ok(); | |||||
| } | |||||
| [Route("~/publishWithTransactionUsingAdonet")] | |||||
| public async Task<IActionResult> PublishMessageWithTransactionUsingAdonet([FromServices]ICapPublisher publisher) | |||||
| { | |||||
| var connectionString = ""; | |||||
| using (var sqlConnection = new SqlConnection(connectionString)) | |||||
| { | |||||
| sqlConnection.Open(); | |||||
| using (var sqlTransaction = sqlConnection.BeginTransaction()) | |||||
| { | |||||
| // your business code | |||||
| publisher.Publish("xxx.services.account.check", new Person { Name = "Foo", Age = 11 }, sqlTransaction); | |||||
| sqlTransaction.Commit(); | |||||
| } | |||||
| } | |||||
| return Ok(); | |||||
| } | |||||
| } | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| ### Subscribe | |||||
| **Action Method** | |||||
| Add the Attribute `[CapSubscribe()]` on Action to subscribe message: | |||||
| ```c# | |||||
| public class PublishController : Controller | |||||
| { | |||||
| [CapSubscribe("xxx.services.account.check")] | |||||
| public async Task CheckReceivedMessage(Person person) | |||||
| { | |||||
| Console.WriteLine(person.Name); | |||||
| Console.WriteLine(person.Age); | |||||
| return Task.CompletedTask; | |||||
| } | |||||
| } | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| **Service Method** | |||||
| If your subscribe method is not in the Controller,then your subscribe class need to Inheritance `ICapSubscribe`: | |||||
| ```c# | |||||
| namespace xxx.Service | |||||
| { | |||||
| public interface ISubscriberService | |||||
| { | |||||
| public void CheckReceivedMessage(Person person); | |||||
| } | |||||
| public class SubscriberService: ISubscriberService, ICapSubscribe | |||||
| { | |||||
| [CapSubscribe("xxx.services.account.check")] | |||||
| public void CheckReceivedMessage(Person person) | |||||
| { | |||||
| } | |||||
| } | |||||
| } | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| Then inject your `ISubscriberService` class in Startup.cs | |||||
| ```c# | |||||
| public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) | |||||
| { | |||||
| //Note: The injection of services needs before of `services.AddCap()` | |||||
| services.AddTransient<ISubscriberService,SubscriberService>(); | |||||
| services.AddCap(x=>{}); | |||||
| } | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| ### Dashboard | |||||
| CAP 2.1 and above provides the dashboard pages, you can easily view the sent and received messages. In addition, you can also view the message status in real time on the dashboard. | |||||
| In the distributed environment, the dashboard built-in integrated [Consul](http://consul.io) as a node discovery, while the realization of the gateway agent function, you can also easily view the node or other node data, It's like you are visiting local resources. | |||||
| ```c# | |||||
| services.AddCap(x => | |||||
| { | |||||
| //... | |||||
| // Register Dashboard | |||||
| x.UseDashboard(); | |||||
| // Register to Consul | |||||
| x.UseDiscovery(d => | |||||
| { | |||||
| d.DiscoveryServerHostName = "localhost"; | |||||
| d.DiscoveryServerPort = 8500; | |||||
| d.CurrentNodeHostName = "localhost"; | |||||
| d.CurrentNodePort = 5800; | |||||
| d.NodeId = 1; | |||||
| d.NodeName = "CAP No.1 Node"; | |||||
| }); | |||||
| }); | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| The default dashboard address is :[http://localhost:xxx/cap](http://localhost:xxx/cap) , you can also change the `cap` suffix to others with `d.MatchPath` configuration options. | |||||
| 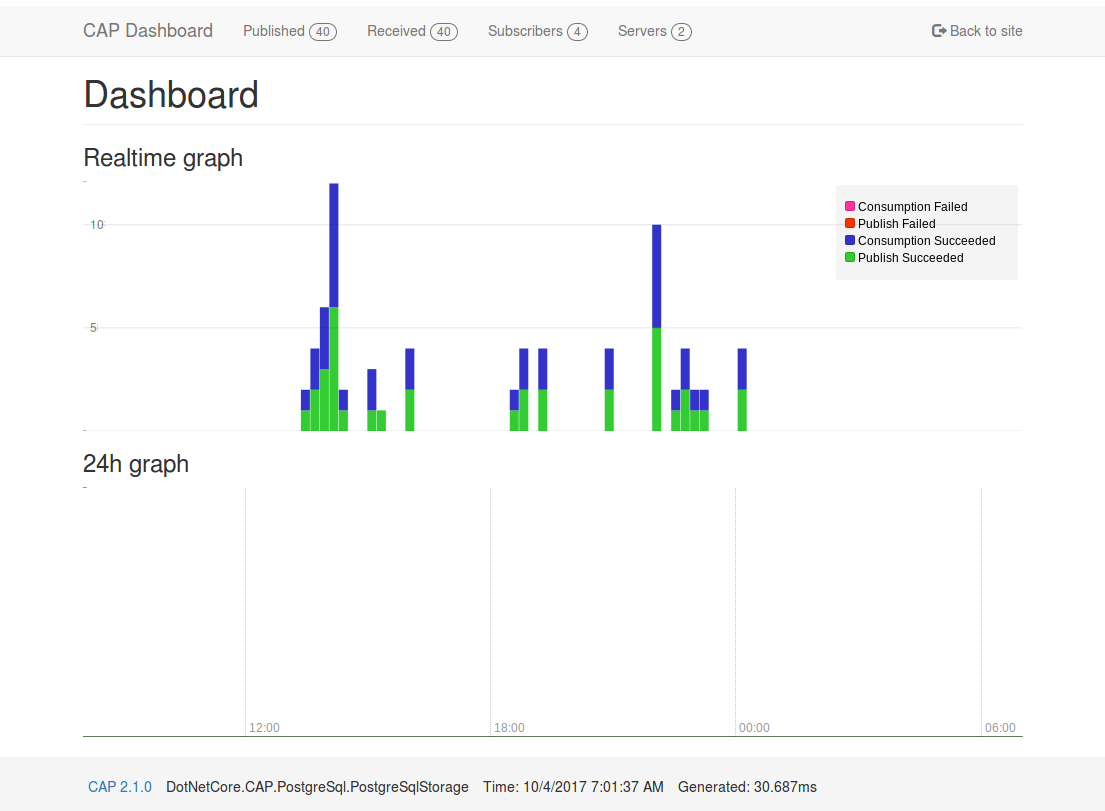 | |||||
| 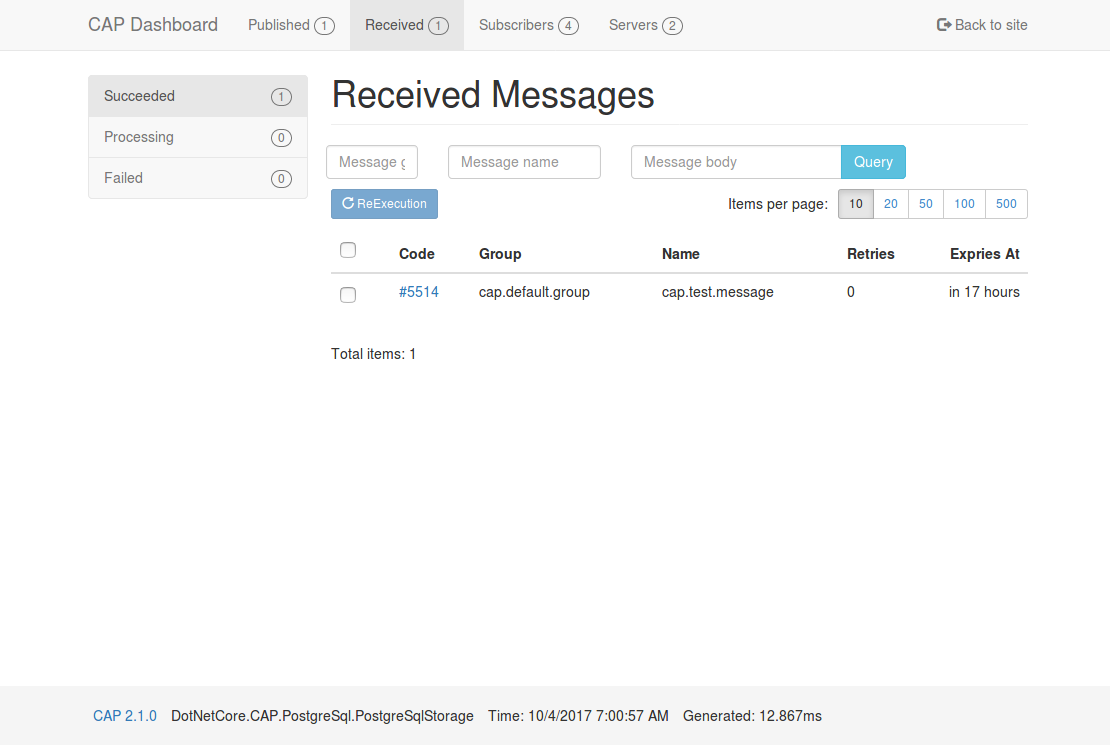 | |||||
| 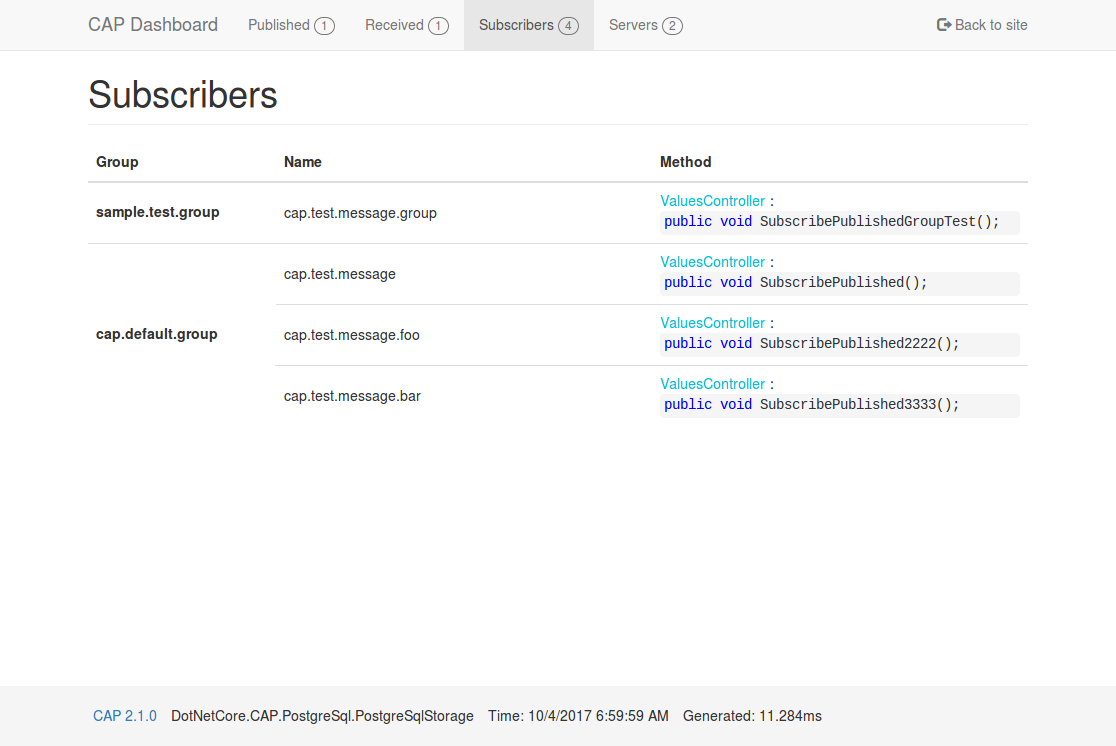 | |||||
| 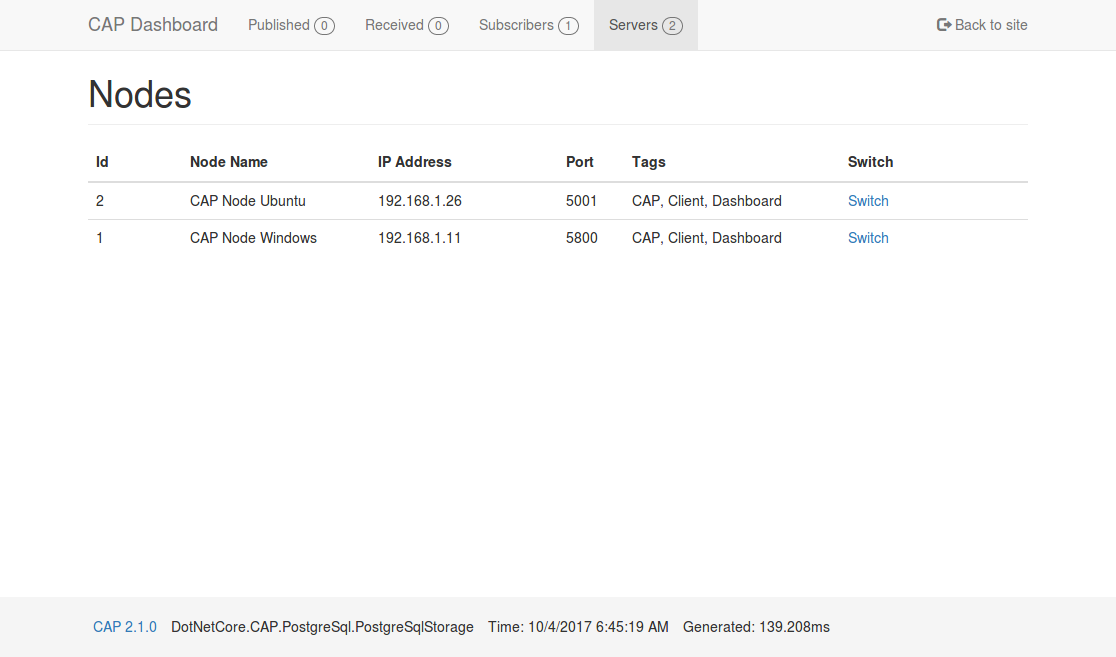 | |||||
| ## Contribute | |||||
| One of the easiest ways to contribute is to participate in discussions and discuss issues. You can also contribute by submitting pull requests with code changes. | |||||
| ### License | |||||
| [MIT](https://github.com/dotnetcore/CAP/blob/master/LICENSE.txt) | |||||
+ 40
- 53
README.md
View File
| @@ -16,9 +16,7 @@ You can also use the CAP as an EventBus. The CAP provides a simpler way to imple | |||||
| This is a diagram of the CAP working in the ASP.NET Core MicroService architecture: | This is a diagram of the CAP working in the ASP.NET Core MicroService architecture: | ||||
|  | |||||
| > The solid line in the figure represents the user code, and the dotted line represents the internal implementation of the CAP. | |||||
|  | |||||
| ## Getting Started | ## Getting Started | ||||
| @@ -30,27 +28,22 @@ You can run the following command to install the CAP in your project. | |||||
| PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP | PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP | ||||
| ``` | ``` | ||||
| If you want use Kafka to send integrating event, installing by: | |||||
| CAP supports RabbitMQ and Kafka as message queue, select the packages you need to install: | |||||
| ``` | ``` | ||||
| PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.Kafka | PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.Kafka | ||||
| ``` | |||||
| If you want use RabbitMQ to send integrating event, installing by: | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.RabbitMQ | PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.RabbitMQ | ||||
| ``` | ``` | ||||
| CAP supports SqlServer, MySql, PostgreSql as event log storage. | |||||
| CAP supports SqlServer, MySql, PostgreSql,MongoDB as event log storage. | |||||
| ``` | ``` | ||||
| // select a database provider you are using, event log table will integrate into. | // select a database provider you are using, event log table will integrate into. | ||||
| PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.SqlServer | PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.SqlServer | ||||
| PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.MySql | PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.MySql | ||||
| PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.PostgreSql | PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.PostgreSql | ||||
| PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.MongoDB //need MongoDB 4.0+ cluster | |||||
| ``` | ``` | ||||
| ### Configuration | ### Configuration | ||||
| @@ -62,18 +55,21 @@ public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) | |||||
| { | { | ||||
| //...... | //...... | ||||
| services.AddDbContext<AppDbContext>(); | |||||
| services.AddDbContext<AppDbContext>(); //Options, If you are using EF as the ORM | |||||
| services.AddSingleton<IMongoClient>(new MongoClient("")); //Options, If you are using MongoDB | |||||
| services.AddCap(x => | services.AddCap(x => | ||||
| { | { | ||||
| // If you are using EF, you need to add the following configuration: | |||||
| // Notice: You don't need to config x.UseSqlServer(""") again! CAP can autodiscovery. | |||||
| x.UseEntityFramework<AppDbContext>(); | |||||
| // If you are using EF, you need to add the configuration: | |||||
| x.UseEntityFramework<AppDbContext>(); //Options, Notice: You don't need to config x.UseSqlServer(""") again! CAP can autodiscovery. | |||||
| // If you are using ado.net,you need to add the configuration: | |||||
| // If you are using Ado.Net, you need to add the configuration: | |||||
| x.UseSqlServer("Your ConnectionStrings"); | x.UseSqlServer("Your ConnectionStrings"); | ||||
| x.UseMySql("Your ConnectionStrings"); | x.UseMySql("Your ConnectionStrings"); | ||||
| x.UsePostgreSql("Your ConnectionStrings"); | x.UsePostgreSql("Your ConnectionStrings"); | ||||
| // If you are using MongoDB, you need to add the configuration: | |||||
| x.UseMongoDB("Your ConnectionStrings"); //MongoDB 4.0+ cluster | |||||
| // If you are using RabbitMQ, you need to add the configuration: | // If you are using RabbitMQ, you need to add the configuration: | ||||
| x.UseRabbitMQ("localhost"); | x.UseRabbitMQ("localhost"); | ||||
| @@ -83,13 +79,6 @@ public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) | |||||
| }); | }); | ||||
| } | } | ||||
| public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app) | |||||
| { | |||||
| //..... | |||||
| app.UseCap(); | |||||
| } | |||||
| ``` | ``` | ||||
| ### Publish | ### Publish | ||||
| @@ -99,38 +88,39 @@ Inject `ICapPublisher` in your Controller, then use the `ICapPublisher` to send | |||||
| ```c# | ```c# | ||||
| public class PublishController : Controller | public class PublishController : Controller | ||||
| { | { | ||||
| [Route("~/publishWithTransactionUsingEF")] | |||||
| public async Task<IActionResult> PublishMessageWithTransactionUsingEF([FromServices]AppDbContext dbContext, [FromServices]ICapPublisher publisher) | |||||
| private readonly ICapPublisher _capBus; | |||||
| public PublishController(ICapPublisher capPublisher) | |||||
| { | { | ||||
| using (var trans = dbContext.Database.BeginTransaction()) | |||||
| { | |||||
| // your business code | |||||
| _capBus = capPublisher; | |||||
| } | |||||
| //If you are using EF, CAP will automatic discovery current environment transaction, so you do not need to explicit pass parameters. | |||||
| //Achieving atomicity between original database operation and the publish event log thanks to a local transaction. | |||||
| await publisher.PublishAsync("xxx.services.account.check", new Person { Name = "Foo", Age = 11 }); | |||||
| [Route("~/adonet/transaction")] | |||||
| public IActionResult AdonetWithTransaction() | |||||
| { | |||||
| using (var connection = new MySqlConnection(ConnectionString)) | |||||
| { | |||||
| using (var transaction = connection.BeginTransaction(_capBus, autoCommit: true)) | |||||
| { | |||||
| //your business code | |||||
| trans.Commit(); | |||||
| _capBus.Publish("xxx.services.show.time", DateTime.Now); | |||||
| } | |||||
| } | } | ||||
| return Ok(); | return Ok(); | ||||
| } | } | ||||
| [Route("~/publishWithTransactionUsingAdonet")] | |||||
| public async Task<IActionResult> PublishMessageWithTransactionUsingAdonet([FromServices]ICapPublisher publisher) | |||||
| [Route("~/ef/transaction")] | |||||
| public IActionResult EntityFrameworkWithTransaction([FromServices]AppDbContext dbContext) | |||||
| { | { | ||||
| var connectionString = ""; | |||||
| using (var sqlConnection = new SqlConnection(connectionString)) | |||||
| using (var trans = dbContext.Database.BeginTransaction(_capBus, autoCommit: true)) | |||||
| { | { | ||||
| sqlConnection.Open(); | |||||
| using (var sqlTransaction = sqlConnection.BeginTransaction()) | |||||
| { | |||||
| // your business code | |||||
| publisher.Publish("xxx.services.account.check", new Person { Name = "Foo", Age = 11 }, sqlTransaction); | |||||
| //your business code | |||||
| sqlTransaction.Commit(); | |||||
| } | |||||
| _capBus.Publish(""xxx.services.show.time", DateTime.Now); | |||||
| } | } | ||||
| return Ok(); | return Ok(); | ||||
| } | } | ||||
| } | } | ||||
| @@ -146,12 +136,10 @@ Add the Attribute `[CapSubscribe()]` on Action to subscribe message: | |||||
| ```c# | ```c# | ||||
| public class PublishController : Controller | public class PublishController : Controller | ||||
| { | { | ||||
| [CapSubscribe("xxx.services.account.check")] | |||||
| public async Task CheckReceivedMessage(Person person) | |||||
| [CapSubscribe("xxx.services.show.time")] | |||||
| public void CheckReceivedMessage(DateTime datetime) | |||||
| { | { | ||||
| Console.WriteLine(person.Name); | |||||
| Console.WriteLine(person.Age); | |||||
| return Task.CompletedTask; | |||||
| Console.WriteLine(datetime); | |||||
| } | } | ||||
| } | } | ||||
| @@ -170,11 +158,10 @@ namespace xxx.Service | |||||
| public void CheckReceivedMessage(Person person); | public void CheckReceivedMessage(Person person); | ||||
| } | } | ||||
| public class SubscriberService: ISubscriberService, ICapSubscribe | public class SubscriberService: ISubscriberService, ICapSubscribe | ||||
| { | { | ||||
| [CapSubscribe("xxx.services.account.check")] | |||||
| public void CheckReceivedMessage(Person person) | |||||
| [CapSubscribe("xxx.services.show.time")] | |||||
| public void CheckReceivedMessage(DateTime datetime) | |||||
| { | { | ||||
| } | } | ||||
| } | } | ||||
| @@ -196,7 +183,7 @@ public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) | |||||
| ### Dashboard | ### Dashboard | ||||
| CAP 2.1 and above provides the dashboard pages, you can easily view the sent and received messages. In addition, you can also view the message status in real time on the dashboard. | |||||
| CAP v2.1+ provides the dashboard pages, you can easily view the sent and received messages. In addition, you can also view the message status in real time on the dashboard. | |||||
| In the distributed environment, the dashboard built-in integrated [Consul](http://consul.io) as a node discovery, while the realization of the gateway agent function, you can also easily view the node or other node data, It's like you are visiting local resources. | In the distributed environment, the dashboard built-in integrated [Consul](http://consul.io) as a node discovery, while the realization of the gateway agent function, you can also easily view the node or other node data, It's like you are visiting local resources. | ||||
